Want to ace your cybersecurity exams? A structured daily study routine is your best bet. Research shows consistent study habits can boost exam scores by 33%. Instead of cramming, commit to 2–3 focused hours daily, spread across reading, practice, and review sessions. Break your study into manageable chunks, use active recall techniques, and prioritize hands-on labs for real-world skills.
Here’s a quick breakdown of an effective routine:
- Morning: Start with hydration, light exercise, mindfulness, and a 10-minute review of yesterday’s notes. Tackle tough topics early while your energy is high.
- Midday: Focus on hands-on labs and practical tools like Wireshark and Nmap.
- Afternoon: Address weak areas using practice tests and active recall strategies.
- Evening: Reinforce learning with flashcards and spaced repetition. Reflect on progress and plan the next day.
Take regular breaks to stay sharp, eat a balanced lunch, and aim for 8–9 hours of sleep to retain what you learn. Staying consistent and adjusting based on practice test results ensures steady progress toward exam success.
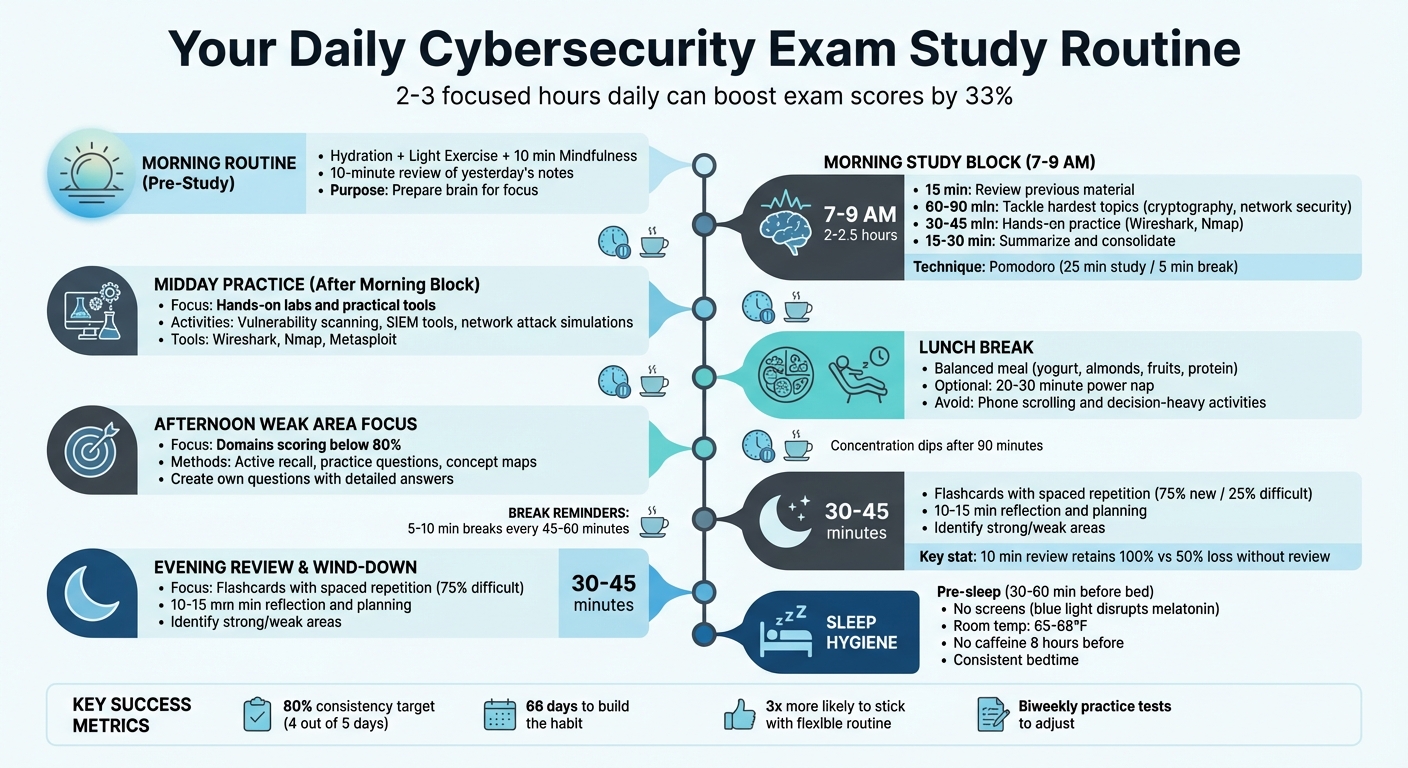
Daily Cybersecurity Study Routine Schedule with Time Blocks
How to Study for Cybersecurity (Even When You're Busy!)
Morning Routine: Set Up Your Study Day
A well-structured morning routine can sharpen your focus and boost memory retention without adding extra hours to your study schedule.
Hydration, Exercise, and Mindfulness
Kick off your day with a glass of water. Even mild dehydration can make it harder to concentrate. After that, get your body moving with some light exercise. Activities like a brisk walk, stretching, or a quick workout release dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin - chemicals that enhance both focus and memory. Plus, exercise increases oxygen flow to the brain and strengthens neural connections. Wrap up this part of your routine with 10 minutes of mindfulness. This helps fine-tune your attention, preparing you for tackling more complex topics later. Once you're centered, take a few minutes to reinforce your learning by reviewing previous notes.
Review Yesterday's Notes
Dedicate 10 minutes to revisiting what you studied the day before. This simple habit helps shift information from short-term to long-term memory, especially since sleep plays a key role in consolidating new knowledge. But don’t just skim through your notes - actively engage with the material. Start by summarizing key ideas from memory, then compare your recall with your notes to identify any gaps. This method of active retrieval is far more effective for creating lasting memories.
As Scott H Young explains: "A ten-minute pop-quiz on previous topics can save hours of cramming".
Core Study Blocks: Focus and Practice
Once your morning warm-up wraps up, it’s time to dive into focused study sessions. Breaking your work into manageable blocks that include reading, practice, and hands-on labs can keep your mind sharp and help fend off mental fatigue. By smoothly transitioning from warm-up exercises to focused study, you’re reinforcing a solid exam preparation routine.
Morning Study Block (7–9 AM)
Kick off your day with the toughest material while your energy is at its peak. Organize this session into clear segments:
- 15 minutes for reviewing what you’ve already learned.
- 60–90 minutes to tackle new topics like cryptography or network security.
- 30–45 minutes for hands-on practice using tools like Wireshark or Nmap.
- 15–30 minutes to summarize and consolidate what you’ve covered.
As ISC2 puts it: "Eat the frog: tackle the domain giving the most trouble first. From there, the rest of the domains are more likely to be a piece of cake."
To keep your focus sharp, try the Pomodoro Technique: 25 minutes of studying followed by a 5-minute break. Eliminate distractions by turning off non-essential Wi-Fi and silencing notifications.
Midday Practice and Labs
The midday session is perfect for diving into hands-on work. At this point, your mental energy is well-suited for tackling complex lab exercises. Use browser-based labs to practice skills like vulnerability scanning, working with SIEM tools, and simulating network attacks - all without needing to set up complicated local environments. Focus on mastering tools commonly used in the field, such as Wireshark, Nmap, and Metasploit. As you work through each lab, make sure to document every step to reinforce your learning and understanding.
Afternoon Weak Area Focus
Use the afternoon to zero in on areas where you’re struggling, based on practice test results. If you’re scoring below 80% in any domain, dedicate this time to that subject. Create your own questions and craft detailed answers - this active recall method strengthens your memory and understanding.
To make the most of this session, incorporate different learning methods. For instance, use text-to-speech apps to review notes, draw concept maps to connect ideas like network security protocols, or explain tricky topics aloud to a study partner. Keeping a learning journal can also help you track which problems challenge you the most and how you overcome them. These strategies not only solidify your knowledge but also build confidence in tackling tough material.
sbb-itb-8a31326
Breaks and Recharge: Prevent Burnout
Did you know that after about 90 minutes of studying, your concentration starts to dip? Pushing past this point often leads to reduced productivity and mental fatigue. The trick is to take breaks before you hit that wall.
As the University of Rochester Learning Center explains: "Taking a break before I felt it was needed because waiting until I felt it was needed might be too late."
Incorporating regular breaks into your study routine can help you stay focused and productive throughout the day.
Short Breaks Between Study Sessions
Plan for a 5–10 minute break every 45–60 minutes. During these short pauses, step away from your desk and do something unrelated to studying. Stretch, try a few yoga poses, or take a quick walk around your space. These activities can help reduce stress and improve both your mood and creativity.
One important tip: skip your phone during breaks. Research shows that scrolling through social media or browsing the web during downtime can actually drain the same mental energy you need for studying, leaving you more fatigued. Instead, focus on activities that give your brain a true reset.
Lunch and Power Nap
Your midday break is just as important as those shorter pauses. Fuel your brain with a balanced lunch - think yogurt, almonds, fresh fruits, or a protein bar. These foods help stabilize blood sugar levels, keeping your focus steady. After eating, consider taking a 20–30 minute power nap. Studies show that a quick nap can refresh your mind and prevent your performance from slipping during long study days.
If naps aren’t your thing, use this time for light physical activity. Take a longer walk or do some gentle stretching to recharge. Just steer clear of activities that require a lot of decision-making, like online shopping or choosing a movie to watch. These can drain the mental energy you’ll need for tackling complex cybersecurity concepts later. Keep your lunch break simple and stress-free, avoiding any heavy conversations that might make it harder to refocus afterward.
Evening Review and Wind-Down
Reviewing your material in the evening helps lock in what you've learned. Studies reveal that without reviewing within 24 hours, you could forget about 50% of what you studied. By 30 days, that number might plummet to just 5%. However, spending a quick 10 minutes reviewing the next day can help you retain nearly 100% of the information, cutting future review time to just 2–4 minutes by day 30.
Spaced Repetition and Flashcards
Flashcards work best when paired with active recall - actively pulling information from memory instead of passively flipping through them. Use flashcards to focus on essential terms (like ARP, DNS, or SMTP) and split your review time wisely: dedicate 75% to new material and 25% to revisiting tricky topics. Before diving into your flashcards, try the "blank page test." Grab a blank sheet and write down everything you can remember about a topic, such as "Incident Response Phases." This exercise highlights what you already know and what needs more attention.
Once you've wrapped up your review, take a moment to reflect on your progress and prepare for the next day.
Reflect and Plan for Tomorrow
After reinforcing your learning with flashcards, spend 10–15 minutes reflecting on your day. Identify which areas of cybersecurity felt solid and which concepts tripped you up. If you can’t simplify a complex topic onto an index card or a quick reference sheet, that’s a sign to revisit it tomorrow. Use this time to plan the next day with clear, actionable goals. For example, instead of vague targets like “study cryptography,” aim for something specific like “Complete 50 Security+ practice questions” or “Review three chapters on cryptography.”
To set yourself up for a restful night, keep a notebook by your bed to jot down lingering thoughts or to-do items. This simple habit can help clear your mind and make it easier to fall asleep.
Sleep Hygiene
Sleep is non-negotiable if you want to retain what you’ve studied. Aim for 8–9 hours of sleep to allow your brain to process and store new information during REM sleep. Skimping on sleep cuts into this critical stage. To prepare for restful sleep, disconnect from screens 30–60 minutes before bed. Blue light disrupts melatonin production, making it harder to fall asleep. Create an ideal sleep environment: keep your room cool (65–68°F), dark, and quiet. Avoid caffeine at least 8 hours before bedtime - its effects can linger and disrupt your sleep, even hours later.
Establish a calming 30-minute wind-down routine. Low-impact activities like reading a physical book, stretching, meditating, or taking a warm bath can signal your body that it’s time to relax. A warm shower followed by a quick cooldown mimics the natural drop in body temperature that promotes sleepiness. Finally, stick to a consistent bedtime and wake-up time - even on weekends. This routine helps regulate your body’s internal clock, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up refreshed.
Conclusion: Stay Consistent and Adjust as Needed
Building a daily study routine isn't about aiming for perfection - it’s about showing up consistently and making smart tweaks along the way. Strive for 80% consistency; even sticking to your plan four out of five days can lead to noticeable progress and help keep stress levels in check.
To stay on track, take biweekly practice tests and dedicate 20 minutes every Sunday to review your results and tweak your schedule. If your scores dip below 80% in any area, adjust your study time to focus on those weaker spots. Using a spreadsheet or journal to log your progress can help you pinpoint areas that need more attention.
As Rob Witcher from Destination Certification says: "Once you're consistently scoring well on practice exams and know the objectives by heart, you're ready."
This ongoing self-assessment paves the way for a weekly review process that keeps your study plan sharp. If a particular topic turns out to be tougher than expected, shift time from areas you’ve already mastered to the ones that need extra focus. This kind of flexibility makes it three times more likely that you’ll stick with your routine over the long haul.
It takes time to build a reliable study habit - about 66 days of consistent effort. When life gets unpredictable, try adopting a "portable routine." For example, if your usual study time doesn’t work one day, fit in 60 minutes after dinner instead. This adaptability helps you stay on course, even when things don’t go as planned.
FAQs
What’s the best way to use active recall for studying cybersecurity?
Active recall is a technique that strengthens your memory by actively retrieving information rather than just reviewing notes or textbooks. Here’s how you can put it into practice:
- Write it out from memory: After studying, put your materials away and write down everything you can remember about the topic. This pushes your brain to work harder, solidifying the information.
- Use flashcards effectively: Create flashcards with a question on one side and the answer on the other. Test yourself by recalling the answer before flipping the card over.
- Turn headings into questions: If a heading says “Phases of Cybersecurity Risk Assessment,” reframe it as a question like, “What are the phases of cybersecurity risk assessment?” Then try to answer it without peeking at your notes.
- Take practice quizzes: Challenge yourself with practice questions or past exam problems. Focus on the areas where you struggle and revisit those topics until you feel confident.
Incorporating these strategies into your study routine can help you retain information more effectively and feel more prepared for your cybersecurity exams. The secret? Stick to it - dedicate a little time each day to active recall, and watch your memory improve!
How can hands-on labs enhance my cybersecurity exam preparation?
Incorporating hands-on labs into your study routine is a game-changer. It bridges the gap between learning concepts and applying them in real-world scenarios. By setting up a home lab, you can experiment with tools, configure networks, and troubleshoot security systems - all in a safe and controlled environment. This practice not only reinforces your knowledge but also helps you retain it longer. Plus, it builds the confidence you need to tackle practical tasks during exams.
On top of that, hands-on experience makes you stand out in the job market. Labs let you apply multiple concepts, sharpen your problem-solving skills, and even create a portfolio of projects to impress potential employers. Dedicating just a few hours each week to practical exercises can give you the edge certification bodies and hiring managers are looking for.
How does sleep affect my ability to prepare for cybersecurity exams?
Sleep is crucial for helping your brain absorb and retain information. During deep sleep, your brain works behind the scenes to strengthen neural connections and move what you've learned into long-term memory. This process makes recalling details - like port numbers or protocol specifics - much easier and sharpens your problem-solving abilities.
When prepping for cybersecurity exams, aim for a consistent sleep schedule of 7–9 hours each night. Research shows that steady sleep patterns boost memory and focus, while late-night cramming with minimal rest can leave you with scattered recall and slower mental responses. To get the most out of your study efforts, combine a well-organized study plan with proper rest. Reviewing key material before bed can also help solidify what you've learned, making sleep an underrated but powerful ally in your exam prep.